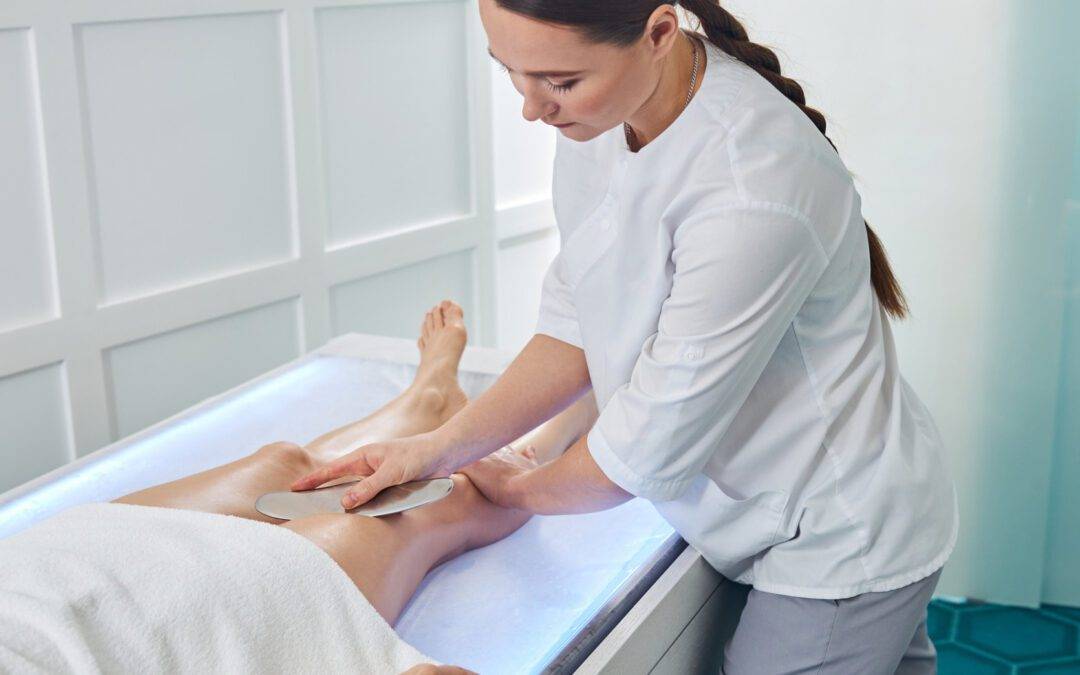
By Megan White, RMT
4 Minute Read
Gua Sha originates from China. It is a scraping technique using tools to scrape over the skin, with lotion or oil, to help release fascia and soft tissues. When the tools are scraped over the skin a mild inflammation response is triggered. That inflammatory response is called hyperemia. Hyperemia is new, oxygen-rich, nutritious blood.
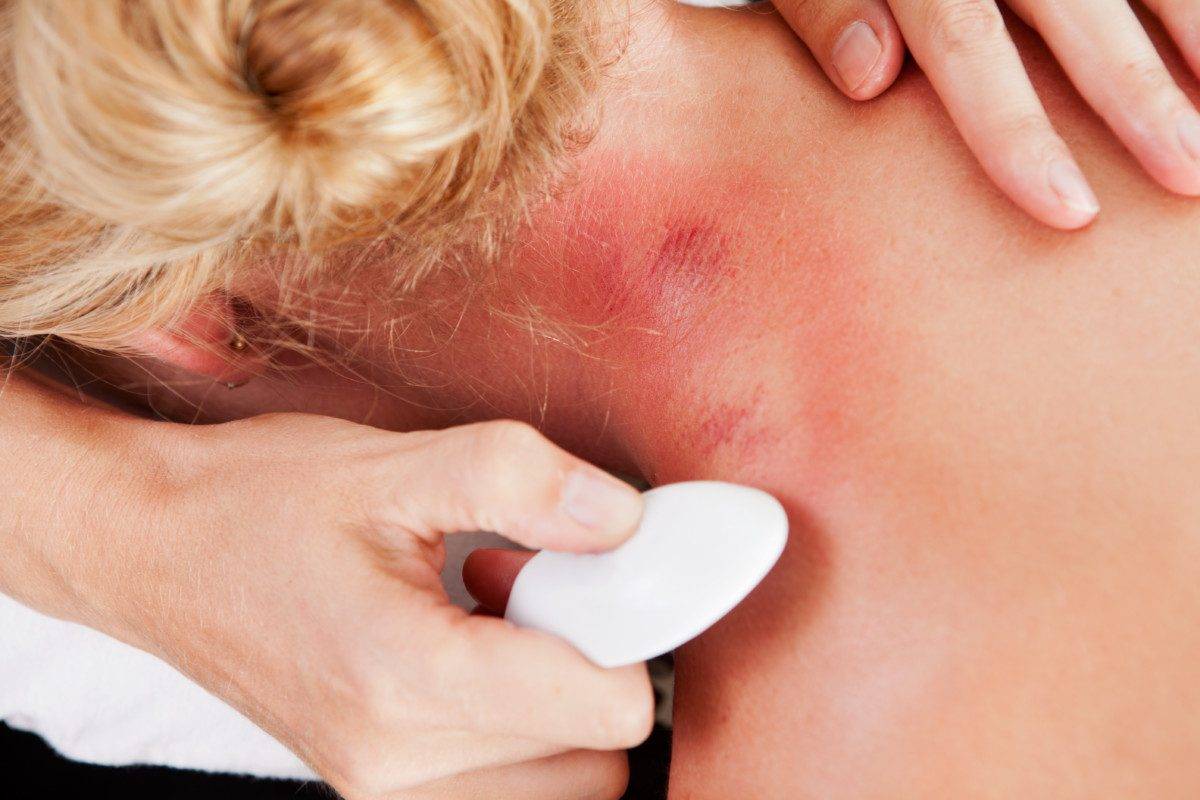
Three different amounts of pressure are used to treat soft tissue dysfunctions. Light pressure is used to just bring that nutrient-rich blood to the area, this is good for patients that do not like a lot of heavy, deep pressure. Medium pressure is the most commonly used and is what should be used in most treatments. The medium pressure brings the blood to the area, decreases scar tissue, and can decrease muscle tension in more superficial muscles. Deep heavy pressure can be applied in more difficult cases when there is intense or very deep muscle tension, this can be uncomfortable and a great deal of communication needs to be had between the therapist and patient to ensure they are okay and no damage is inflicted.
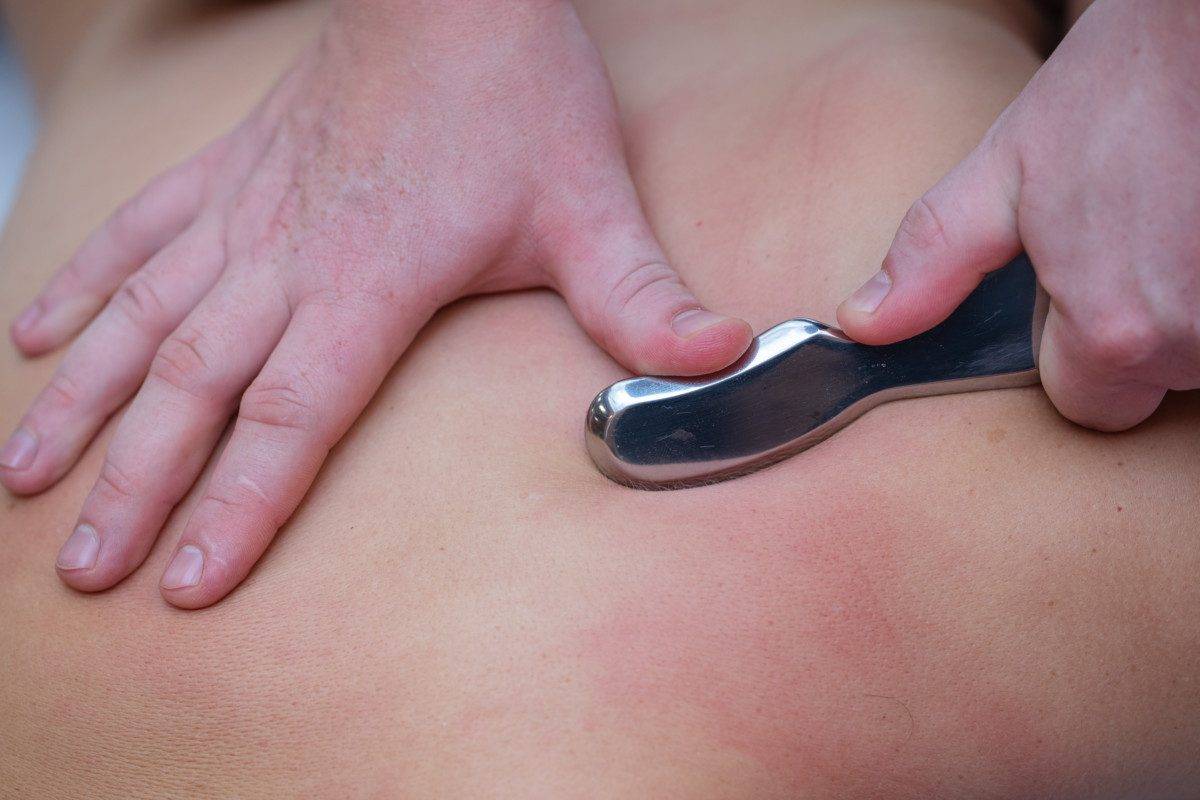
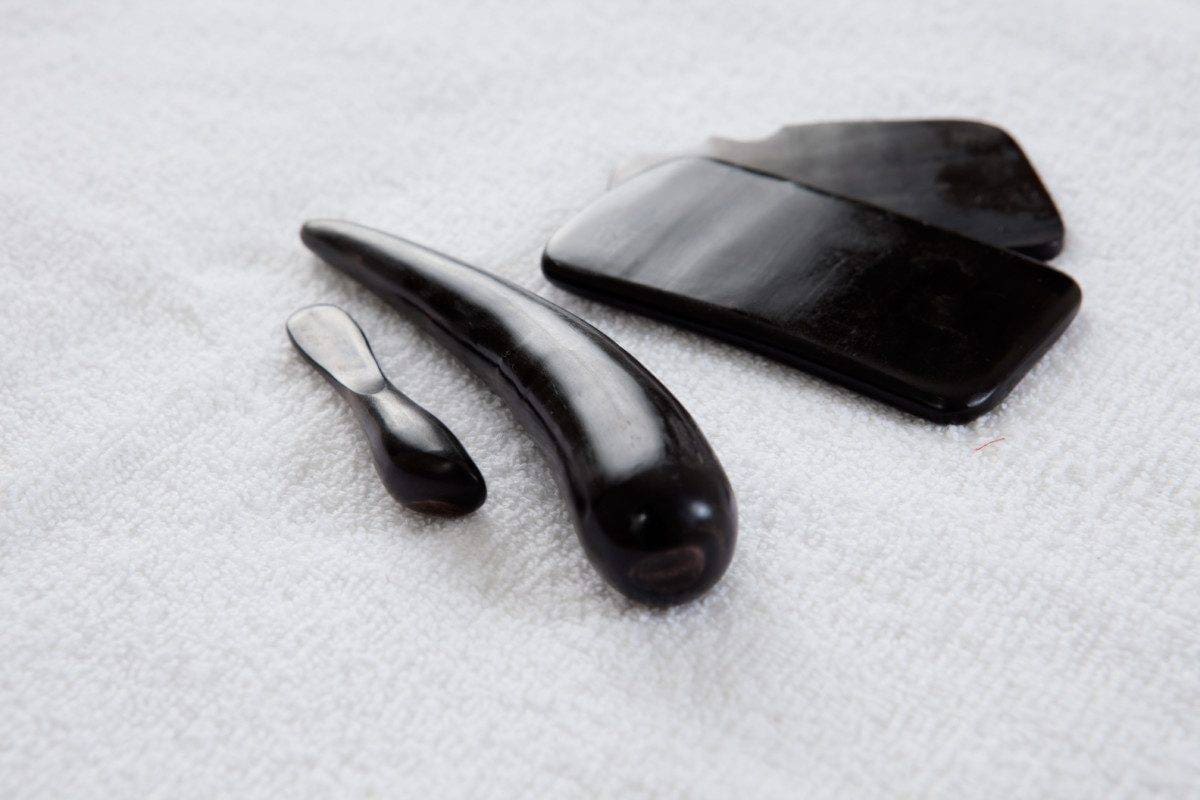
There are many types of tools that can be used in a gua sha treatment. They are made from different materials, such as stone; including jade, quartz, and amethyst. Tools can also be made from stainless steel, titanium, horn, and wood. They come in many shapes and sizes depending on the area being treated and the preference of the therapist.

After receiving treatment with gua sha included it’s likely that a patient will feel more tired than just a treatment without it. A lot of fluids are moved around with the gua sha, like blood and lymphatic fluid, this causes the body to feel more tired than a regular manual therapy treatment would. Following the gua sha treatment, it is suggested to use a cool pack to the areas because of the mild inflammation response that the scraping causes.
Gua sha can greatly benefit many different soft tissue dysfunction, however open communication is very important and if the scraping is not tolerated, let your therapist know.

